Industry 4.0 Security Risks and Opportunities
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is a term used to describe the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing and other industries. This new era of manufacturing is characterised by the use of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics, which enable machines to communicate and share data with one another in order to optimise production processes.
One of the main benefits of Industry 4.0 is increased efficiency and productivity. By using advanced technologies such as IoT and AI, factories can automatically monitor and adjust production processes in real-time, which can lead to a significant reduction in downtime and waste. Additionally, by connecting machines and devices to the internet, factories can easily gather and analyse data, which can be used to optimise production processes and identify potential problems before they occur.
Another key benefit of Industry 4.0 is improved quality control. With the use of advanced sensors and AI algorithms, factories can automatically detect and correct defects in products, which can lead to a significant reduction in the number of defective products being produced.
Additionally, with the ability to connect machines and devices to the internet, factories can easily share data with suppliers and customers, which can help to improve the overall quality of products and services.
In addition to increased efficiency and productivity, Industry 4.0 can also lead to significant cost savings. By using advanced technologies such as IoT and AI, factories can reduce the need for manual labor, which can lead to a reduction in labor costs. Additionally, by using data analysis to optimise production processes and identify potential problems before they occur, factories can reduce the need for expensive repairs and maintenance.
Another benefit of Industry 4.0 is the ability to create new products and services. With the use of advanced technologies such as IoT and AI, factories can easily gather and analyse data, which can be used to identify new opportunities for product development and innovation. Additionally, by connecting machines and devices to the internet, factories can easily share data with suppliers and customers, which can help to identify new opportunities for creating value-added services.
One of the key concerns with Industry 4.0 is the potential impact on jobs. With the increasing use of automation and AI, some jobs may be replaced by machines, which could lead to job loss and unemployment. However, it’s worth noting that Industry 4.0 also creates new jobs, such as data analysts and engineers, that require new skills. Moreover, automation and AI can free up employees from repetitive tasks and allow them to focus on more value-added activities, such as problem-solving, creativity, and customer service.
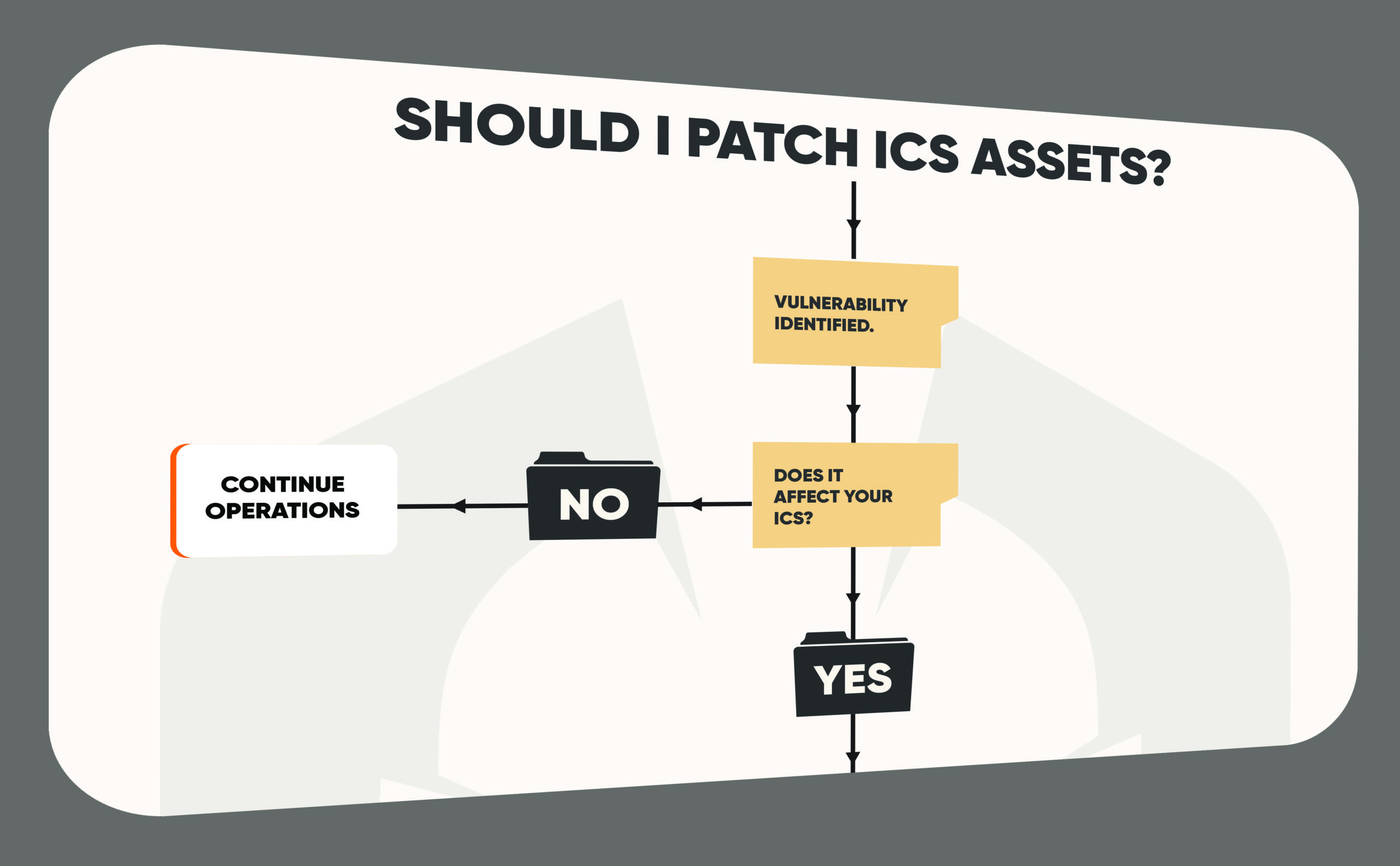
Another concern with Industry 4.0 is the potential impact on privacy and security. With the increasing use of IoT and connected devices, there is a risk that personal data may be collected and used without consent, which could lead to privacy breaches. Additionally, with the increasing use of advanced technologies such as AI, there is a risk that these technologies may be used to create autonomous and dangerous applications.
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 is a term used to describe the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing and other industries. It has many benefits including increased efficiency and productivity, improved quality control, cost savings, and the ability to create new products and services. However, there are also concerns such as potential job loss and privacy and security risks. It’s important for policymakers, businesses, and individuals to be aware of these potential impacts and take steps to mitigate them. Industry 4.0 presents a great opportunity for the manufacturing sector to be more efficient, productive, and innovative, but it also requires a responsible approach to ensure it benefits all stakeholders.