React Less. Defend More.
Hyper-Realistic Cyber Defence Training
Sharpen your cyber skills on a cyber range.
Simulate live cyberattacks. Be prepared for real ones.
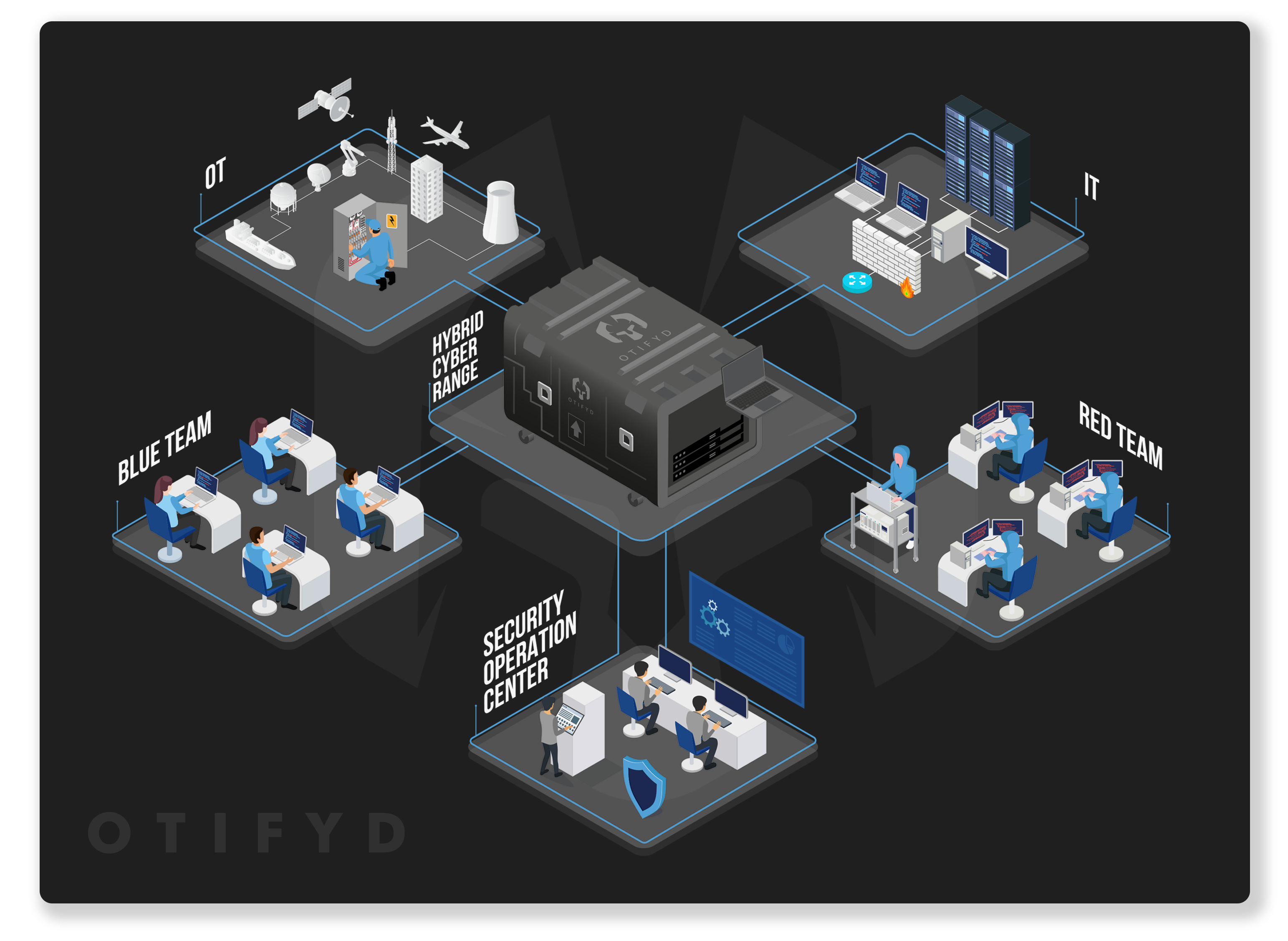
OTIFYD Cyber Ranges
OTIFYD, in collaboration with leading cyber range companies, offers a cutting-edge cybersecurity skill development platform that stands at the forefront of immersive training experiences. Our cyber ranges empower organisations to cultivate elite cyber defence teams by providing a hyper-realistic virtual arena that closely mirrors real-world cyber attack scenarios.
With our cyber ranges, participants are immersed in dynamic and challenging environments where they face simulated cyber threats, attacks, and incidents. These scenarios are meticulously designed to replicate the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by real adversaries, offering an unparalleled opportunity for hands-on learning and skill development.
We offer customisable training programs tailored to the specific needs and objectives of organisations. Whether it’s industry-specific challenges, compliance requirements, or unique cybersecurity goals, our platform can be customised to address a wide range of training needs.
The Four Pillars of a Hyper-Realistic Training
Perfected over years, OTIFYD offers a comprehensive platform providing your cyber defence team with all essential
elements for replicating the cyberattack experience.
Real-World Networks
The cyber range and 100% live and simulates networks of massive scale, mirroring the complexity and diversity of real-world networks found in enterprises and organisations.
Real-World Cyberattacks
In our Hyper-Realistic cyber range, participants experience reverse-engineered malware and the full cyber kill chain, preparing them to defend against real-world threats.
Real-World Tools
Participants access top security tools, gaining practical Real-world hands-on experience. They develop proficiency and effectively utilising these tools for threat detection and network defence.
Real-World Assessment
Cyber Ranges provide a more accurate assessment than theoretical knowledge using advanced analytics with real-time feedback, enabling participants to identify areas for improvement efficiently.
Hyper-Realistic Cyber Range Attack Simulation
OTIFYD offers the world’s most advanced cyber range, available on-demand. Immerse your team in hyper-realistic, simulated attacks on the included cyber range to take their experience, skillset, and teamwork to the next level. OTIFYD’s live-fire cyber range simulations are the closest your team will get to a real-world incident. By training in cyber range exercises your team will excel, both technically and mentally, when the real attack takes place.
One of the Largest Catalog of On-Demand Attacks
Access one of the world’s largest catalog of on-demand cyberattacks on the included cyber range, ensuring your team can recognise and respond to any attacker technique, tactic, or procedure. Live-Fire scenarios on OTIFYD’s Cyber Range are suited for Red, Blue, or Purple Teams and range in difficulty from beginner to advanced.
Live Fire Attacks, in the Cloud
Experience attack simulations based on vulnerabilities found in ICS / OT, Cloud and IT native and hybrid environments. With new environments come new assets, network components and attacker behaviors your team needs to be prepared to defend your cloud assets. Ensure your team is prepared to detect, investigate, and mitigate with complete live-fire attack scenarios, ensuring they can respond at an elite level.
Train with the Tools You Use Daily
Your security stack is only as good as the people who use it. OTIFYD’s Cyber Range exercises provide your team with a suite of commercial tools they’d actually use on the job to ensure they can perform investigations using a SIEM such as Splunk or Qradar and a Networks Firewall technologies such as Fortinet, Palo Alto or Checkpoint, practice reconfiguring Firewalls to remediate an attack, or use their tools to accomplish any other task.
Comprehensive Corporate Grade Networks
OTIFYD’s Cyber Range exercises run on corporate-grade virtual networks so they can reflect the challenges your team will face during incident detection, investigation and response. The comprehensive network architectures included on the cyber range allows your team to experience advanced attacker behaviors they may encounter on the job, like ping sweeps, lateral movement and data exfiltration, providing your team with the experience required to excel.
Prepare for Attacks on ICS/OT Networks
Simulate attacks on operational technology (OT) networks to maximise your skills in defending critical physical infrastructure such as power grids, water and wastewater plant, pharmaceutical, manufacturing lines, oil and gas, and more. OTIFYD provides a full-scale, emulated OT network, including HMIs, hardware controllers (PLCs), and physical devices, and provides end-to-end simulations of IT to OT attacks.
Choose the Right Deployment For You.
On-premise Training
Deploy Cyber Range on-premises using your own hardware and VMware. The platform can be air-gapped for top security or network integrated for accessible via a web browser.
Hosted Self-paced Cloud
Start training in minutes with our cloud-based Cyber Range. No special equipment necessary—just a web browser and an internet connection.
Instructor-led Cloud
Start training in minutes with our cloud-based Cyber Range. No special equipment necessary—just a web browser and an internet connection.
What is a Cyber Range?
Cyber ranges are specialised environments designed to simulate real-world cybersecurity scenarios and provide a platform for training, testing, and exercising cybersecurity skills and capabilities. These environments typically consist of virtualised or physical networks, systems, and applications that mimic the infrastructure and operations of an organisation’s IT environment.
Key features of cyber ranges include:
Training and Education: Cyber ranges offer a controlled environment where cybersecurity professionals can develop and refine their skills through hands-on training exercises. They provide opportunities to learn about various cybersecurity concepts, tools, techniques, and best practices in a practical setting.
Exercises and Simulations: Cyber ranges facilitate the simulation of cyber attacks, incidents, and scenarios to assess and improve preparedness, response, and resilience. These exercises may involve red teaming, blue teaming, penetration testing, incident response drills, and other simulations to test defences, detect threats, and practice response procedures.
Skill Development: Cyber ranges help individuals and teams build and enhance their technical and non-technical cybersecurity skills, including threat detection, incident analysis, malware analysis, network forensics, digital forensics, and decision-making under pressure.
Collaboration and Competition: Cyber ranges often support collaborative and competitive activities, where participants can work together or compete against each other to achieve specific objectives, solve challenges, and improve performance. This fosters teamwork, communication, and camaraderie among cybersecurity professionals.
Customisation and Flexibility: Cyber ranges can be customised to simulate various environments, scenarios, and threat actors relevant to specific industries, organisations, or training objectives. They offer flexibility in configuring networks, systems, and challenges to meet the unique needs and requirements of participants.
Assessment and Evaluation: Cyber ranges provide mechanisms for assessing and evaluating participants’ performance, skills, and capabilities during training exercises and simulations. This feedback helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, enabling continuous learning and development.
What is a Cyber Range exercise?
A cyber range exercise is a structured and controlled activity conducted within a cyber range environment to simulate real-world cybersecurity scenarios, test defences, and enhance the skills and capabilities of cybersecurity professionals. These exercises typically involve various participants, including red teams (attackers), blue teams (defenders), and sometimes purple teams (combinational roles or oversight).
Key elements of a cyber range exercise include:
Scenario Development: Exercises are designed based on specific cybersecurity scenarios, such as a simulated cyber attack, data breach, ransomware incident, or network intrusion. Scenarios may vary in complexity and objectives, tailored to the training goals and skill levels of participants.
Team Roles and Responsibilities: Participants are assigned to different teams, each with specific roles and responsibilities. Red teams act as adversaries, attempting to infiltrate systems, exploit vulnerabilities, and achieve specific objectives, while blue teams defend against these attacks, detect threats, and respond to incidents.
Simulation Environment: Cyber range exercises take place within a simulated environment that mimics the infrastructure, systems, applications, and networks of a real-world organisation. This environment may include virtualised or physical systems, network segments, and security tools.
Rules of Engagement: Exercises are conducted according to predefined rules of engagement (ROE) that outline the scope, objectives, constraints, and guidelines for participants. ROE help ensure a controlled and safe environment for conducting the exercise while maintaining realism and relevance.
Scenario Execution: Participants execute the scenario by performing actions aligned with their roles and objectives. Red teams may attempt to penetrate defenses, exploit vulnerabilities, escalate privileges, and exfiltrate data, while blue teams work to detect, analyse, and respond to these threats in real-time.
Debriefing and Feedback: Following the exercise, participants engage in debriefing sessions to review and discuss their performance, lessons learned, best practices, and areas for improvement. Feedback from instructors, observers, or automated systems helps participants identify strengths and weaknesses and develop action plans for enhancing their skills and capabilities.
How do you build a Cyber Range?
Building a cyber range involves several steps to create a simulated environment where cybersecurity training exercises and simulations can take place. Here’s a general overview of how to build a cyber range:
Define Objectives and Requirements: Determine the goals and objectives of the cyber range, including the types of training exercises and simulations you want to conduct, the target audience (e.g., cybersecurity professionals, students), and the technical requirements of the range (e.g., hardware, software, networking).
Select a Platform: Choose a platform or software solution for building and managing the cyber range environment. There are various commercial and open-source platforms available, each offering different features and capabilities. Examples include Cyberbit Range, RangeForce, and Open Cyber Challenge Platform (OCCP).
Design the Environment: Design the cyber range environment to simulate realistic scenarios and challenges. This may involve setting up virtual machines, networks, applications, and systems that mimic the infrastructure of a real-world organisation. Consider factors such as network segmentation, system configurations, and security controls.
Implement Security Controls: Implement security controls and measures to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the cyber range environment. This includes configuring firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), antivirus software, and other security tools to protect against unauthorised access and malicious activities.
Develop Scenarios and Exercises: Create cybersecurity scenarios and exercises tailored to the objectives of the training program. Scenarios may include simulated cyber attacks, data breaches, malware infections, and other security incidents. Develop realistic objectives, rules of engagement, and success criteria for each exercise.
Provide Training Materials: Develop training materials, documentation, and resources to support participants during the exercises. This may include instructional videos, written guides, reference materials, and hands-on labs to help participants learn and practice cybersecurity concepts and skills.
Conduct Testing and Validation: Test and validate the cyber range environment to ensure it functions as intended and meets the requirements of the training program. Conduct pilot exercises with a small group of participants to identify any issues or areas for improvement.
Deploy and Maintain: Deploy the cyber range environment and make it accessible to participants. Ensure that the environment is properly maintained, updated, and monitored to address security vulnerabilities, software bugs, and performance issues over time.
Evaluate Performance and Feedback: Evaluate the performance of participants during training exercises and gather feedback to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Use this feedback to refine and enhance the cyber range environment and training program.
Continuous Improvement: Continuously assess and improve the cyber range environment and training program based on feedback, emerging threats, and evolving cybersecurity best practices. Regularly update scenarios, exercises, and training materials to keep the training program relevant and effective.
What is Cyber Range as a Service (CRaaS)?
Cyber Range as a Service (CRaaS) is a cloud-based or managed service offering that provides organisations with access to virtualised cyber range environments for cybersecurity training, testing, and exercises. Instead of building and maintaining their own cyber range infrastructure, organisations can subscribe to CRaaS solutions offered by third-party providers to access pre-configured environments, scenarios, and training resources on-demand.
Key features and benefits of Cyber Range as a Service include:
Scalability: CRaaS solutions offer scalability, allowing organisations to scale their cyber range resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility enables organisations to accommodate varying numbers of participants and training exercises without the need for significant upfront investments in infrastructure.
Cost-Effectiveness: By leveraging CRaaS, organisations can avoid the capital expenses associated with building and maintaining their own cyber range infrastructure. Instead, they pay a subscription fee or usage-based pricing model, making it a cost-effective option for organisations of all sizes.
Accessibility: CRaaS solutions are typically accessible via the internet, allowing participants to access the cyber range environment from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility enables remote training and collaboration, making it convenient for distributed teams or individuals to participate in cybersecurity exercises.
Managed Services: CRaaS providers handle the management and maintenance of the cyber range infrastructure, including software updates, security patches, and performance optimisation. This relieves organisations of the burden of managing the infrastructure themselves, allowing them to focus on training and skill development.
Customization: Many CRaaS providers offer customisable environments and scenarios tailored to the specific needs and objectives of organisations. This customisation allows organisations to create training exercises that reflect their unique cybersecurity challenges, industry-specific threats, and compliance requirements.
Training Resources: CRaaS solutions often include a variety of training materials, exercises, and resources to support cybersecurity training and skill development. These may include instructional videos, hands-on labs, simulations, and documentation to help participants learn and practice cybersecurity concepts and techniques.
Realistic Simulations: CRaaS environments are designed to simulate real-world cybersecurity scenarios and challenges, providing participants with a realistic training experience. This realism enhances the effectiveness of training exercises by preparing participants to respond effectively to actual cyber threats and incidents.
What are some benefits of Cyber Ranges for a Blue Team?
The blue team, responsible for defending against cyber threats and ensuring the security of an organization’s systems and networks, can derive several benefits from utilizing a cyber range. Here are some key advantages:
Hands-on Training: Cyber ranges provide a realistic environment for blue team members to gain hands-on experience in defending against simulated cyber threats. This practical training enables them to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, improving their skills and decision-making abilities.
Scenario-Based Learning: Blue teams can engage in scenario-based learning exercises within the cyber range, where they face simulated cyber attacks and incidents. These exercises help them develop effective response strategies, refine incident detection and analysis techniques, and enhance their overall readiness to handle security incidents.
Skill Development: Cyber ranges offer opportunities for blue team members to develop and hone a wide range of technical and non-technical cybersecurity skills. This includes skills such as threat detection, malware analysis, incident response, forensics, network security, and system hardening.
Team Collaboration: Cyber ranges facilitate teamwork and collaboration among blue team members, allowing them to work together to detect, analyze, and respond to cyber threats. Team-based exercises enable participants to share knowledge, coordinate response efforts, and learn from each other’s experiences.
Realistic Scenarios: Cyber ranges simulate realistic cyber threat scenarios, providing blue teams with exposure to a variety of attack techniques, tactics, and procedures. This realism helps blue team members understand the tactics used by adversaries and prepares them to effectively defend against evolving cyber threats.
Continuous Improvement: Cyber ranges support continuous improvement by enabling blue teams to conduct regular training exercises, assess their performance, and identify areas for improvement. Feedback from exercises helps teams refine their processes, procedures, and strategies to enhance their effectiveness over time.
Risk-Free Environment: Cyber ranges offer a safe and controlled environment for blue teams to practice and experiment with different defensive techniques and tools without risking damage to production systems or networks. This allows teams to test new security controls, configurations, and response procedures without fear of causing disruptions or downtime.
Evaluation and Assessment: Cyber ranges provide mechanisms for evaluating and assessing the performance of blue teams during training exercises. Metrics such as detection rates, response times, and effectiveness of countermeasures can be tracked and analyzed to measure progress, identify strengths and weaknesses, and guide improvement efforts.
What are some benefits of Cyber Ranges for a Red Team?
The Red Team, responsible for simulating cyber attacks and testing the effectiveness of an organisation’s defences, can benefit from utilising cyber ranges in several ways. Here are some key advantages:
Realistic Simulation: Cyber ranges provide a realistic environment for Red Team members to simulate cyber attacks against target systems and networks. These simulations closely mimic real-world scenarios, enabling Red Team members to assess the effectiveness of their attack techniques and tactics in a controlled setting.
Skill Development: Cyber ranges offer opportunities for Red Team members to develop and enhance their offensive cybersecurity skills. Through hands-on exercises and simulations, Red Team members can practice techniques such as reconnaissance, exploitation, privilege escalation, lateral movement, and exfiltration in a safe and controlled environment.
Scenario-Based Learning: Red Team members can engage in scenario-based learning exercises within the cyber range, where they face a variety of simulated challenges and objectives. These exercises help Red Team members refine their attack strategies, adapt to changing environments, and improve their overall proficiency in conducting cyber attacks.
Tool Familiarisation: Cyber ranges provide Red Team members with the opportunity to familiarise themselves with a wide range of offensive cybersecurity tools and techniques. Red Team members can experiment with different tools, exploit frameworks, and attack vectors to better understand their capabilities and limitations.
Team Collaboration: Cyber ranges facilitate collaboration and teamwork among Red Team members, allowing them to work together to plan and execute coordinated cyber attacks. Team-based exercises enable Red Team members to share knowledge, coordinate activities, and leverage each other’s expertise to achieve their objectives.
Evaluation and Assessment: Cyber ranges provide mechanisms for evaluating and assessing the performance of Red Team members during training exercises. Metrics such as success rates, time to compromise, and stealthiness of attacks can be tracked and analysed to measure progress, identify areas for improvement, and guide training efforts.
Adversarial Thinking: Cyber ranges help cultivate adversarial thinking among Red Team members, encouraging them to think like real attackers and anticipate the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) adversaries might use. This mindset enables Red Team members to develop more sophisticated attack strategies and better understand the challenges faced by defenders.
Continuous Improvement: Cyber ranges support continuous improvement by enabling Red Team members to conduct regular training exercises, experiment with new attack techniques, and learn from their experiences. Feedback from exercises helps Red Team members refine their tactics, improve their tradecraft, and stay up-to-date with emerging threats and techniques.
What is Purple Teaming?
Purple Teaming is a cybersecurity approach that combines the techniques and perspectives of both offensive (Red Team) and defensive (Blue Team) security teams. The main goal of Purple Teaming is to improve an organisation’s overall security posture by fostering collaboration and information sharing between these two teams.
In a Purple Team engagement, the Red Team (ethical hackers) simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the organisation’s systems and defences, while the Blue Team (defensive security teams) works to detect, respond to, and mitigate these simulated attacks.
The key aspects of Purple Teaming include:
- Collaboration: Red and Blue Teams work together closely, sharing information, techniques, and insights throughout the entire process.
Realistic scenarios: The Red Team launches realistic attacks that mimic the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by real-world threat actors, allowing the Blue Team to practice their detection and response capabilities in a controlled environment. - Continuous improvement: The findings and lessons learned from Purple Team exercises are used to enhance the organisation’s security controls, incident response processes, and overall cyber resilience.
- Knowledge transfer: Purple Teaming facilitates the transfer of knowledge and skills between the Red and Blue Teams, enabling them to better understand each other’s perspectives and improve their respective capabilities.
By fostering collaboration and shared understanding between offensive and defensive teams, Purple Teaming helps organisations identify and address security gaps, validate their security controls, and ultimately strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture.
