React Less. Defend More.
PrivilegeD Access Management-PAM
Protect industrial networks against cyberthreats by monitoring, detecting, and preventing unauthorised privileged access to critical resources.
Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management (PAM) in the industrial environment refers to the processes and systems used to manage, control, and monitor the access to critical systems, applications, and data in industrial facilities such as manufacturing plants, oil and gas refineries, power plants, etc. The main objective of PAM in the industrial environment is to ensure that only authorised personnel have access to critical systems and data, and that all access is tracked, monitored, and audited.
In the industrial environment, PAM can be a critical component in maintaining the security and reliability of control systems and networks, which are often responsible for controlling and monitoring critical infrastructure and equipment. PAM solutions can include access controls, authentication systems, and audit trails to ensure that only authorised personnel can access systems, applications, and data, and that all access is tracked and monitored.
How industrial Control System that can benefit from PAM
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems: used to monitor and control critical infrastructure such as pipelines, power plants, and manufacturing facilities
Distributed Control Systems (DCS): used to monitor and control processes in industrial facilities such as chemical plants and refineries
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC): used to control and monitor industrial automation systems
Firewall management: Firewalls are essential for controlling access to and from industrial control systems. PAM solutions can be used to manage and monitor the configuration of firewalls, ensuring that they are properly configured to allow only authorized access.
Password management: Passwords are the most common form of authentication in the OT environment. PAM solutions can be used to enforce strong password policies, store passwords securely, and prevent the reuse of passwords.
Role-based access control: PAM solutions can be used to implement role-based access control, which grants access to systems, applications, and data based on the role of the user. This helps ensure that only authorized personnel have access to critical systems and data.
Multi-factor authentication: PAM solutions can be used to implement multi-factor authentication, which requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a smart card. This helps ensure that only authorized personnel have access to critical systems and data.
Monitoring and auditing: PAM solutions can be used to monitor and audit access to critical systems, applications, and data. This includes tracking who has accessed a system, what they did, and when they did it. This information can be used for security investigations and to help ensure compliance with security policies and regulations.
Endpoint security: PAM solutions can be used to secure the endpoints that connect to industrial control systems, such as laptops and workstations. This can include monitoring for malware, enforcing security policies, and preventing unauthorized access.
These are just a few examples of how PAM can be used in the OT environment. It’s important to note that PAM solutions in the OT environment must be designed to meet the unique requirements of these environments, such as the need for high availability and real-time monitoring and control.
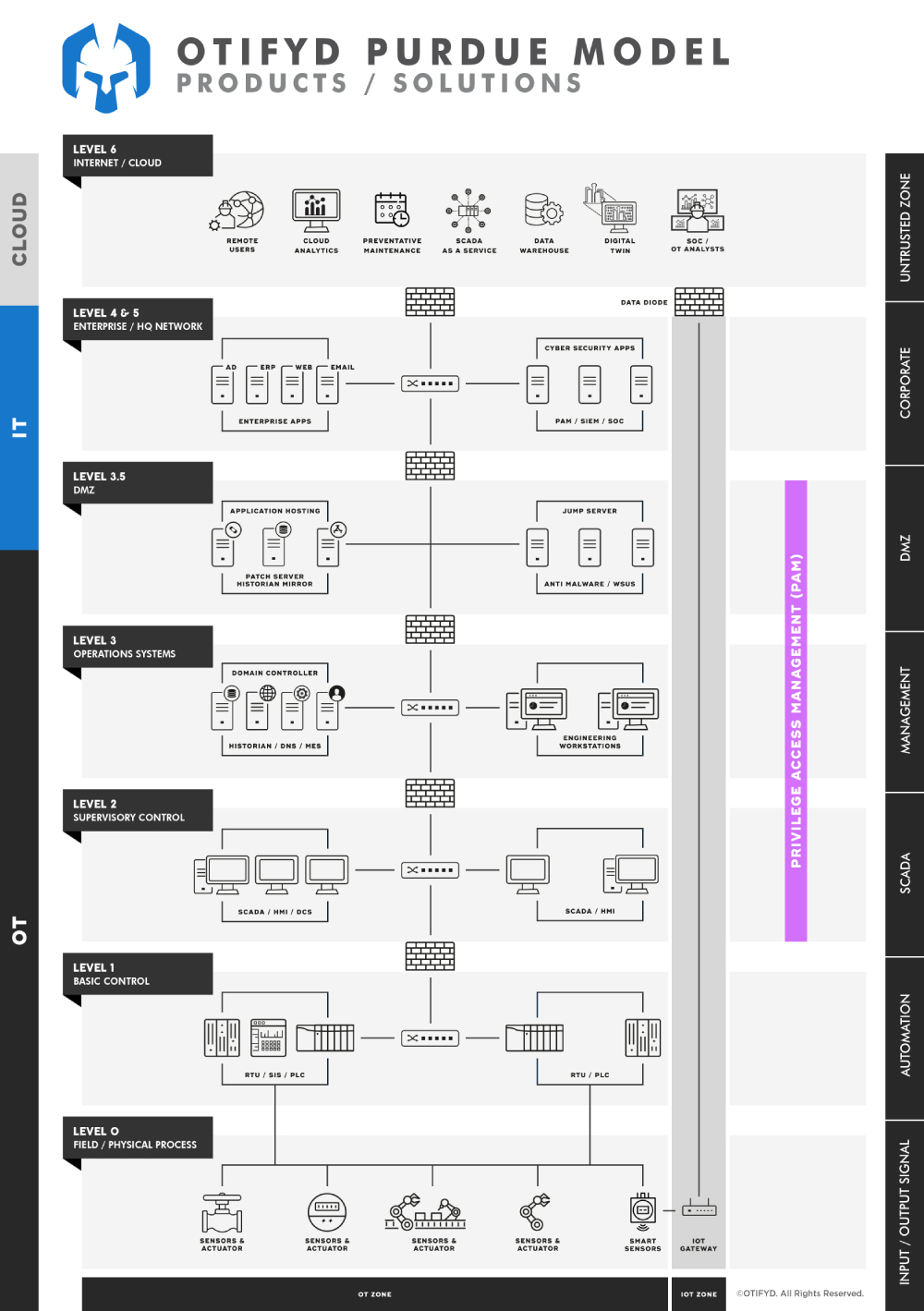
PAM in an industrial control system networks
It’s important to note that PAM solutions for the industrial environment must be designed with the unique requirements of these environments in mind, such as the need for highly available and secure systems, and the requirement for real-time monitoring and control.
PAM is a critical component in ensuring the security and reliability of industrial control systems, applications, and data. It helps organizations maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical systems and data, and helps ensure that only authorised personnel have access to these systems.
Key factors to consider before selecting a PAM solution for an OT environment
When considering choosing a Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution for an operational technology (OT) environment, there are several key factors to consider:
- Integration with OT systems: Ensure that the PAM solution can integrate with the existing OT systems, such as supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and industrial control systems (ICSs).
- Security: Make sure the PAM solution has strong security features, such as encryption, two-factor authentication, and role-based access controls.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the PAM solution as the OT environment may grow over time.
- Ease of use: The PAM solution should be easy to use, as OT environments often have limited IT staff and resources.
- Compliance: Ensure that the PAM solution is compliant with relevant regulations, such as NIST SP 800-53, IEC 62443, and NERC CIP.
- Support for multiple protocols: Make sure the PAM solution supports the protocols used in the OT environment, such as Telnet, SSH, and serial connections.
- Resilience and high availability: Consider the availability and resilience of the PAM solution as downtime in an OT environment can have significant consequences.
- Cost: Evaluate the cost of the PAM solution, including both the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
By considering these factors, you can select a PAM solution that meets the specific requirements of your OT environment and helps to secure and protect your critical infrastructure. To read more about PAM, you can visit the latest Gartner report 2023 for PAM.
Active Directory hardening using PAM
In an operational technology (OT) environment, the integration of Privileged Access Management (PAM) with Active Directory (AD) can provide a centralized and secure method of managing privileged access to critical systems and devices.
By leveraging the capabilities of AD, PAM solutions can centralize the management of user identities, access controls, and authentication policies. This can help to improve security and reduce the risk of cyber attacks by enforcing strong authentication and access controls and providing auditing and reporting capabilities.
Additionally, PAM solutions integrated with AD can provide single sign-on (SSO) capabilities, allowing users to access multiple systems and devices with a single set of credentials, reducing the risk of lost or stolen passwords.
However, the integration of PAM and AD in an OT environment requires careful planning and consideration of factors such as security, scalability, and compliance with industry standards. In addition, it may be necessary to implement additional security measures, such as network segmentation, to protect the OT environment from cyber attacks.
Overall, the integration of PAM and AD in an OT environment can provide improved security, enhanced efficiency, and reduced risk of cyber attacks, while also ensuring compliance with industry standards.
What is PAM in an OT environment?
PAM in an OT environment refers to the management and control of privileged access to critical infrastructure systems and devices in industries such as energy, utilities, and manufacturing.
Why is PAM important for OT environments?
PAM is important for OT environments as it helps to secure and manage privileged access to critical systems and devices, reducing the risk of unauthorised access and cyber attacks.
What are the benefits of using PAM in OT environments?
The benefits of using PAM in OT environments include improved security, reduced risk of cyber attacks, increased efficiency and productivity, compliance with industry standards, and enhanced resilience and availability.
Can PAM solutions be easily implemented in OT environments?
The ease of implementation of PAM solutions in OT environments depends on factors such as the size and complexity of the environment, the number of systems and devices, and the available resources and expertise.
How does PAM improve security in OT environments?
PAM improves security in OT environments by enforcing strong authentication and access controls, reducing the risk of unauthorised access and cyber attacks, and providing auditing and reporting capabilities.
What are the key features of a PAM solution?
Key features of a PAM solution include password management, session recording and monitoring, access control, privilege elevation, and auditing and reporting.
What is session recording and monitoring in PAM?
Session recording and monitoring refers to the process of capturing and monitoring privileged sessions to detect suspicious activity and prevent unauthorised access. PAM solutions record all privileged sessions in real-time and provide detailed audit logs for forensic analysis.
Why session recording is a critical component of PAM in OT environments?
Because it provides a way to monitor and audit activities of privileged users such as administrators, engineers, and technicians who have access to critical systems and industrial control networks.
n an OT environment, any unauthorised or malicious activity can have serious consequences, such as production downtime, safety hazards, or environmental damage. Session recording helps to identify and investigate suspicious behaviour or security incidents, as well as provide evidence for compliance and audit purposes.
