React Less. Defend More.
ot endpoint security
& protection
Endpoint protection is a foundational element in every OT cybersecurity strategy.
Industrial Endpoint Security
Malicious attacks on Industrial Control Systems (ICS) have increased significantly in recent years. As the Stuxnet and BlackEnergy attacks have shown, one infected USB drive or single spear-phishing email is all it takes for attackers to bridge the air gap and penetrate an isolated network. Traditional security is no longer enough to protect industrial environments from cyber threats. As threats targeting critical infrastructure increase, choosing the right advisor and technology partner to secure your systems has never been more important.
Given the potential impact of a security breach in industrial environments, it’s important to have robust and reliable industrial endpoint security solutions in place to protect critical assets and processes from cyber attacks.
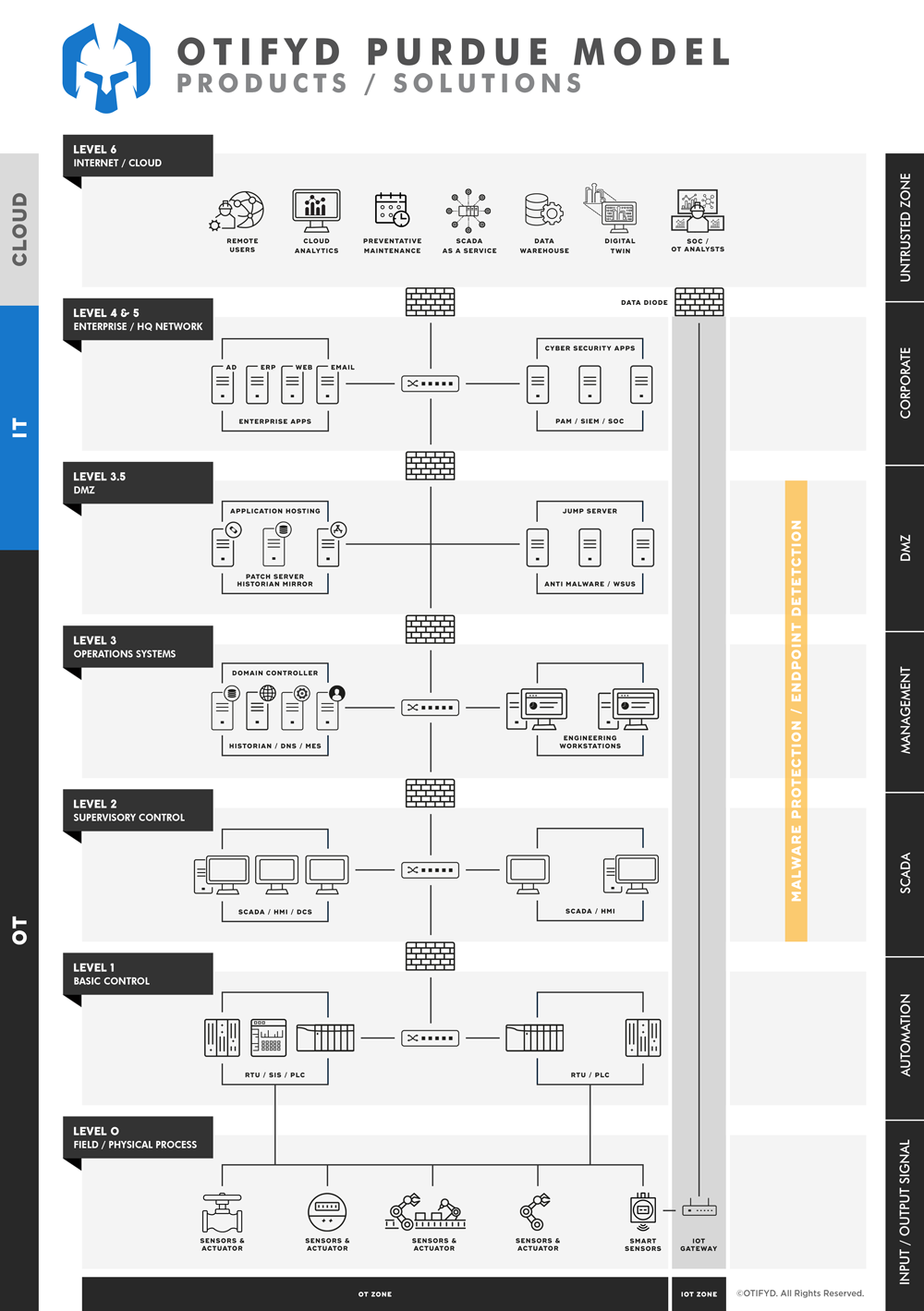
Industrial Endpoint Security refers to the protection of operational technology (OT) devices and systems used in industrial and critical infrastructure environments. These devices are often part of the control systems that run critical processes in manufacturing, energy, water, transportation, and other industries, and they are typically different from traditional IT systems in terms of architecture, networking, and usage.
Industrial Endpoint Security aims to safeguard these devices and systems from cyber threats such as malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches that could compromise the integrity and availability of critical operations. This involves implementing security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and secure communications protocols to monitor, detect, and respond to potential threats.
ICS Purpose-Built Anti Malware
Typically most plants usually need to accommodate legacy endpoints in their Operational Technology (OT) environment, which must interconnect and work well with their many different assets. Traditional antivirus solutions are not designed for the ICS environment as constant virus signature updates require an internet connection while intrusive file scans require a lot of processing power and can easily interfere with operations. Endpoint Protection in an operational environment requires a different spectrum of consideration. There, security must never jeopardise routine operations, slow down computation, or delay decisions made in the plant production processes.
ICS Purpose-Built Anti-Malware refers to specialized software that is specifically designed to protect industrial control systems (ICS) and other operational technology (OT) devices from malicious software, also known as malware.
Traditional anti-malware solutions, which are typically designed for IT systems, may not be suitable for ICS environments because they can interfere with the real-time operations and critical processes that are required in these environments. In contrast, ICS Purpose-Built Anti-Malware is designed to minimize the impact on system performance while providing comprehensive protection against malware and other cyber threats.
These solutions often use a combination of signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, and heuristics to identify and prevent malware infections. They also typically provide detailed reporting and analysis capabilities to help organizations understand the types of threats they are facing and how to respond effectively.
ICS Purpose-Built Anti-Malware is an essential component of a comprehensive industrial endpoint security strategy, as it helps to ensure the safety and reliability of critical systems and processes in industrial and critical infrastructure environments.
Security teams at organisations operating industrial facilities often have limited visibility into OT networks—not just from an asset identification perspective but also when it comes to threats targeting Industrial Control Systems (ICS). IT security tools are not optimised for OT environments and are based on different technologies, protocols, policies, and skills, with unique consequences that require different approaches.
There is an increasing demand for security teams to have a broader converged view that provides more holistic coverage of the entire network, including IT and OT.
This means security teams must face the challenge of supporting unfamiliar technology, systems, and threats while maintaining efficient workflows. The potential risk to businesses is magnified as threats to ICS increase in frequency and sophistication—with potentially significant consequences.
It is critical to provide analysts with improved, complete situational awareness and decision-making support as efficiently as possible.
Difference between Anti Virus and Anti Malware
Antivirus software is designed to detect and remove viruses from a computer system. Viruses are malicious programs that are designed to replicate and spread themselves to other computers. They can cause a wide range of problems, from minor annoyances like pop-ups and slow performance to more serious issues like data loss and system crashes. Antivirus software typically works by scanning files and programs for known virus signatures and then quarantining or deleting any infected files.
Anti-malware software, on the other hand, is designed to detect and remove a wider range of malicious software, including viruses, spyware, adware, and other types of malware. Malware is a broad term that refers to any type of software that is designed to cause harm to a computer system or steal data. Anti-malware software typically uses a combination of signature-based and behavior-based detection methods to identify and remove malicious software.
One key difference between antivirus and anti-malware software is the scope of their protection. While antivirus software is focused specifically on detecting and removing viruses, anti-malware software provides more comprehensive protection against a wider range of threats. Anti-malware software may also include additional features like real-time scanning, automatic updates, device control, and web protection to help protect against online threats like phishing and malicious websites.
Here are some of the key features of good ICS anti-malware solutions:
Real-time protection: The ability to detect and prevent malware infections in real-time is essential in ICS environments, where a security breach could have a significant impact on operations.
Minimal impact on system performance: Good ICS anti-malware solutions are designed to have minimal impact on system performance, so as not to interfere with the real-time operations that are required in these environments.
Signature-based detection: Signature-based detection is a well-established method of identifying known malware by matching it to a database of known signatures. Good ICS anti-malware solutions should include this feature.
Behavioral analysis and heuristics: In addition to signature-based detection, good ICS anti-malware solutions should also use behavioral analysis and heuristics to detect and prevent zero-day and unknown malware.
Reporting and analysis: Good ICS anti-malware solutions should provide detailed reporting and analysis capabilities, so organizations can understand the types of threats they are facing and respond effectively.
Secure communication: Good ICS anti-malware solutions should also include secure communication capabilities, to protect against eavesdropping and tampering of data in transit.
Support for legacy and multiple platforms: Given the wide range of different devices and systems used in ICS environments, good ICS anti-malware solutions should be able to support a range of different platforms and operating systems.
Easy deployment and management: Good ICS anti-malware solutions should be easy to deploy and manage, so organizations can quickly and effectively protect their critical systems and processes from cyber threats.
What is OT malware?
OT malware refers to malware that targets operational technology (OT) systems, which are the hardware and software systems used to control and monitor physical devices and processes in critical infrastructure such as power plants, water treatment facilities, and manufacturing plants.
OT malware is different from traditional IT malware that targets information systems and can have more severe consequences. For example, an OT malware attack could potentially cause physical damage to equipment or disrupt critical processes, leading to safety risks or financial losses.
It is important for organizations to implement robust security measures to protect their OT systems from malware attacks, as these systems are often connected to the internet and can be vulnerable to cyber threats. This may include implementing firewalls, updating software and firmware, monitoring network traffic, and providing regular security training to employees.
Why do we need malware protection for OT environments?
There are several reasons why malware protection is important for operational technology (OT) environments:
- Critical Infrastructure: OT systems are often used to control and monitor critical infrastructure such as power plants, water treatment facilities, and manufacturing plants. If these systems are compromised by malware, it could have serious consequences such as physical damage to equipment, disruption of critical processes, and safety risks to workers and the public.
- Connectivity: Many OT systems are now connected to the internet, which makes them vulnerable to cyber threats. This increased connectivity has made it easier for malware to spread within an organization and to other systems, increasing the risk of a successful attack.
- Lack of Security Awareness: OT environments were not originally designed with cybersecurity in mind, and as a result, many organizations may not be aware of the security risks associated with these systems. This can result in a lack of proper security measures and increased vulnerability to malware attacks.
- High Consequence: OT malware can cause significant financial losses and disruption to critical processes. In some cases, it can also lead to safety risks for workers and the public, making it essential to have adequate protection in place.
Do we need endpoint protection for ICS environments?
Yes, endpoint protection is important for industrial control systems (ICS) environments. Endpoint protection refers to security measures that are implemented on individual devices such as computers, servers, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) within an ICS network.
Endpoint protection can help to prevent malware infections and other types of cyber threats that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ICS systems. This can include measures such as anti-virus software, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
In ICS environments, endpoint protection can help to prevent malware from spreading from infected devices to other parts of the network, reducing the risk of a successful attack. It can also help to detect and prevent malicious activity in real-time, reducing the risk of data loss or disruption to critical processes.
Does malware protection stop ransomware in OT?
Malware protection can help to prevent and stop ransomware attacks in operational technology (OT) environments. However, it is important to note that no single security measure can provide complete protection against all types of cyber threats, including ransomware.
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts the files on an infected device and demands payment from the victim in exchange for a decryption key. To protect against ransomware, organizations should implement multiple layers of security measures, including:
Endpoint protection: This can include anti-virus software, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. These measures can help to prevent ransomware infections by blocking malicious payloads, detecting suspicious network activity, and alerting security teams to potential threats.
Network security: This can include implementing firewalls, network segmentation, and access controls to restrict access to sensitive systems and data. These measures can help to prevent ransomware from spreading across the network and limit the impact of an attack.
Data backup and recovery: Regular data backups can help organizations to recover from a ransomware attack without paying the ransom. This is important in OT environments where the loss of data or disruption to critical processes can have serious consequences.
Security Awareness Training: Regular training for employees on cyber threats and best practices can help to reduce the risk of a successful attack by reducing the risk of human error.
Can we use IT endpoint security in the OT environment?
IT endpoint security solutions can be used in the operational technology (OT) environment, but they may need to be adapted to meet the unique requirements of these systems.
OT environments have different characteristics compared to IT environments, including differences in network architecture, device types, and regulatory requirements. As a result, IT endpoint security solutions may need to be modified to ensure compatibility and effectiveness in an OT environment.
Additionally, some IT endpoint security solutions may not be suitable for use in an OT environment due to the potential impact of security measures on the performance and reliability of these systems. For example, certain anti-virus software may use too much processing power on a device, causing it to slow down or crash, which could disrupt critical processes.
Is ICS anti malware different than IT malware protection?
Yes, industrial control systems (ICS) anti-malware solutions are different from traditional IT anti-malware solutions. ICS systems have unique characteristics compared to IT systems, and require specialized anti-malware solutions to meet the specific requirements of these environments.
Some differences between ICS anti-malware and IT anti-malware include:
- Real-time requirements: ICS systems often require real-time responses to changing conditions, and traditional anti-malware solutions can negatively impact system performance. ICS anti-malware solutions are designed to minimize the impact on system performance and ensure that the system continues to operate in real-time.
- Different device types: ICS systems often use specialized devices such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, which have different requirements compared to traditional IT devices. ICS anti-malware solutions are designed to support these specialized devices and ensure that security measures do not interfere with their operation.
- Regulatory requirements: ICS systems are subject to different regulatory requirements compared to IT systems, and anti-malware solutions for these environments must meet these requirements.
- Different threat landscape: The threat landscape for ICS systems is different from that of IT systems, with a focus on threats that can cause physical harm to equipment and personnel. ICS anti-malware solutions are designed to address these unique threats and ensure the security of these systems.
